While shopping for an air purifier, you may have encountered the term activated carbon filter. You may also have learned that these filters can eliminate VOCs and odors from your indoor air but don’t know how they work.
Below we will explain what activated carbon filters are and take a deeper look into how it works.
- What Is An Activated Carbon Filter?
- How is Carbon Activated?
- How Does Activated Carbon Filter Work?
- Where Do Carbon Filters Excel?
- Types of Activated Carbon Filters
- Factors Influencing Adsorption Capacity in Filters
What Is An Activated Carbon Filter?
An activated carbon filter is an air purification element consisting of a porous carbonaceous material sourced from carbon-rich plants like wood, coconut shells, and tree barks. It can also originate from lignite and bituminous coal.

This material is subsequently taken through an activation process that makes it extremely porous. In fact, one gram of activated carbon can have a surface area of 500m2 and above. This gives it an exponential capacity to eliminate most airborne contaminants, including allergens and odors, with utmost efficiency.
How is Carbon Activated?
There are two methods for activating carbon:
Chemical Activation
Chemical activation involves preparing a bath of acid or chemicals and submerging the carbon into the liquid. The bath is heated to raise its temperatures between 842°F and 1652°F (450 to 900 degrees Celsius).
This process is much quicker than gas treatment. However, caution is exercised as a lot of adsorption occurs in the heating chamber, resulting in an impure active carbon. The carbon may also be useless depending on the quantity of chemical adsorbed.
Gas Treatment
This activation method is achieved by heating the carbon in a chamber while pumping gas. The process exposes the carbon material to oxygen for oxidation purposes. Gas treatment must occur in an inert environment whose temperature ranges between 1112°F and 1652°F (600-900 degrees Celsius).
The chamber is consequently heated to raise the temperature to 1652°F-2192°F (900 and 1200 degrees Celsius). This process causes oxygen to bond to the carbon’s surface, making it an excellent filter for cleaning air or water of pollutants.
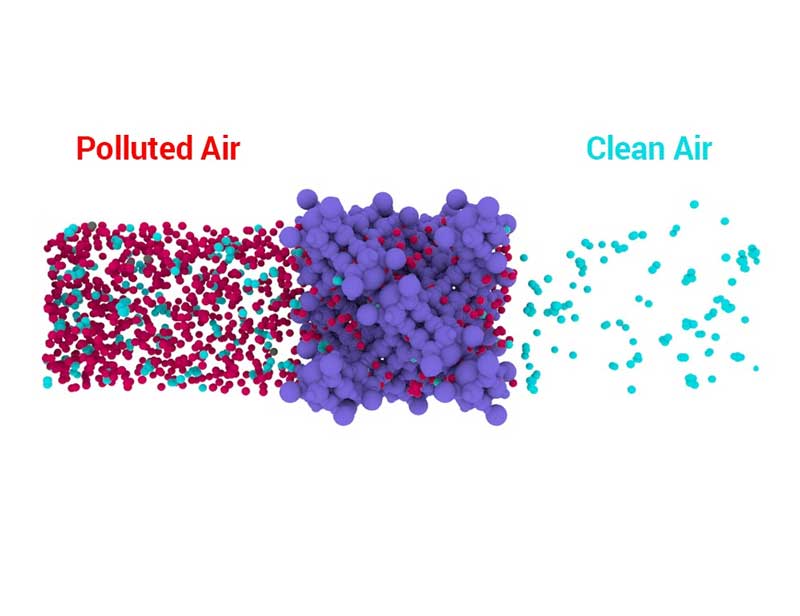
How Does Activated Carbon Filter Work?
Activated carbon filters eliminate airborne contaminants through a process known as adsorption. Simply put, this process provides compounds with an attractive place to reside rather than circulating in the air. Adsorption is often confused with absorption, but the two terms are different.
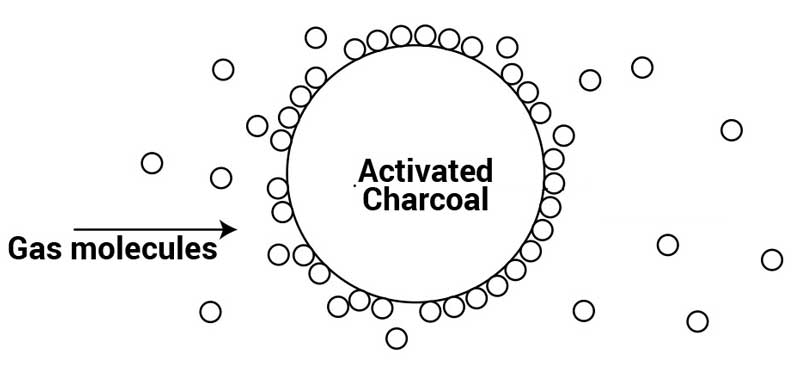
With absorption, the trapped substances are locked inside the absorbent material. On the other hand, adsorption is a process through which the pollutants stick outside the carbon molecules.
This is where activation comes in handy; it increases the adsorption surface of the carbon molecules to maximize a filter’s purification capacity.
Where Do Carbon Filters Excel?
Carbon filters are generally good at trapping tiny particulates measuring below 0.3 micrometers. As such, they are capable of cleaning gaseous pollutants.
Tobacco Smoke
Tobacco smoke contains over 7000 chemicals, with at least 250 of them adversely affecting human health, which is where carbon filters come in handy. Smoke particles measure between 0.1 and 1 microns, meaning that they can pass through a HEPA filter. This makes an activated carbon filter a must-have for people who smoke cigarettes or live with smokers.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
VOCs means molecular-level pollutants that are measured in Picometers, which are smaller than microns. These contaminants are so small that they can remain airborne for a very long period. The only way to remove them from your indoor air is through a high-end activated carbon filter.
VOCs are responsible for the lingering chemical odors you sometimes encounter in your home. Some of the commonly found VOCs in homes include:
- Acetaldehyde—Emanates from burning wood or tobacco products
- Benzene—This one has a sweet odor and usually comes from paint thinners, cleaning products, and glues
- Chloroform—Comes from chlorinated products like bleach
- Formaldehyde—This chemical is introduced into your home via household items like furniture and building materials
- Napthalene—Originates from mothballs
- Styrene—Stems from plastic packaging of appliances, toys, and furniture
- Trichloroethylen—Found in carpet cleaners, varnishes, paints, and spot removers
Note: Ideally, you will want to run your air purifier with an activated carbon filter every time you introduce something new into your home. It’s also advisable to run it after turning off your fireplace.
Odors
Thanks to their ability to trap extremely tiny particulates, carbon activated filters are the perfect tools for eliminating that lingering bad smell from your home. This makes air purifiers with carbon filters appropriate for homes with pets, smokers, or generally people who appreciate the smell of fresh air. They also go a long way in eliminating unpleasant fragrances.
Types of Activated Carbon Filters
Below are four of the commonest activated carbon filters used in air purifiers:
Granular Activated Carbon
Also known as GAC, this filter consists of large granules with a 3mm diameter, the size of small rocks or sand. GAC filters have long service life and can be used in combination with other substances like zeolite. They’re particularly suitable for eliminating odors and gaseous pollutants like formaldehyde.
Powdered Activated Carbon
This filter consists of granules measuring 10 to 50 microns. These granules are bonded together with resins to create one large block. Due to the smaller particles, this filter has a faster and higher adsorption capacity than its granular-activated counterpart.
Woven Carbon Filter
With this filter, activated carbon is woven into rayon fiber to create a cloth. This air cleaner manifests as a thin sheet of carbon filter in your air purifier. It may also come as a standalone unit that you can attach to areas requiring purification, including diaper disposal containers or kitchen waste bins.
Treated Carbon (Impregnation)
Sometimes, carbon is treated with potassium permanganate or silver to enhance its adsorption capacity in a process popularly known as impregnation. Impregnated filters can eliminate a wider range of chemical gasses, such as natural gas and formaldehyde.
Factors Influencing Adsorption Capacity in Filters
While activated carbon filters are very effective in eliminating odors and gaseous pollutants from your indoor air, their efficiency is affected by the following factors:
Temperature
The ideal operating temperature for carbon filters is around 104°F (40 degrees Celsius). If the temperature goes too high, the adsorption rate is adversely affected. On the flip side, high temperatures can potentially cause desorption, a process through which the filter releases previously adsorbed pollutants.
Residence Time
Residence time is the period taken by the air to pass through the carbon filter. This is when the filter adsorbs airborne contaminants; the duration should be as long as possible.
To maximize residence time, the thickness of the carbon filter must be sufficient, and the airflow speed should be kept at a minimum. This means that it’s best to run your air purifier on the low fan setting.
Humidity
Relative humidity has a direct effect on the efficacy of a carbon filter. If your indoor RH levels go beyond 60%, the water molecules in the air will be adsorbed, leaving limited space for the pollutants’ adsorption.
To prevent this, avoid using your air purifier in overly damp rooms like bathrooms. It’s also advisable to use a dehumidifier to maintain ideal RH levels in your indoor space. A moisture extractor with a smart humidistat will go a long way in ensuring that the relative humidity in your home doesn’t go beyond the recommended level.
The Filter’s Age
With continuous use, gaseous pollutants eventually fill up the adsorption sites, making the filter ineffective in trapping more contaminants. Suppose the available space fills up and you fail to replace the filter. In that case, the trapped chemicals with a high adsorption affinity will disperse those with lesser affinity, causing them to recirculate into your indoor air. This is why you must observe carbon filters’ shelf life.
Also, an improperly stored carbon filter could become less efficient with time as it continues to adsorb gases and humidity from the air. This makes it ineffective even before use. As such, it’s imperative to ensure that your replacement filter is fresh and properly stored.
- There’s no perfect method for determining the right time to replace your filter, but you may sometimes notice a smell emanating from your air cleaner
- You won’t necessarily get a sign; it’s best to replace your filter according to the manufacturer’s guidelines
- Also, consider replacing the filter more frequently if your home is exposed to a lot of pollutants
- Ideally, you may replace the filter once a month if your space has high levels of gaseous pollutants like VOCs, smoke, and odors.
Pre-Filters
A pre-filter comes in handy in protecting your activated carbon filter from particles that may cause untimely clogging. As such, ensure that your air purifier comes with at least one superior-quality pre-filter, but more will be appreciated.
Key Takeaway
Activated carbon filters can eliminate more airborne pollutants than their conventional counterparts, which explains their rising popularity among homeowners.
These filters have a high adsorption rate and hence the perfect choice for eliminating tiny particulates like VOCs, odors, and smoke from your indoor air. Activated carbon filters can be used as standalone air cleaners. They can also be installed in air purifiers to improve the machines’ purification capacity.
